Personalized medicine facilitates the creation of specific therapies tailored to each individual's genetic code, such as tissue regeneration using stem cells, gene therapies to correct harmful mutations, and the development of diagnostic tests to identify and mitigate genetic health risks.
Complex pathologies often require precise therapeutic approaches due to their limited treatment margins. Genetic characterization of these diseases helps to select the most appropriate drugs or to create molecular targets for the development of new drugs.
Detailed study of the genome enables the development of highly precise treatments by understanding the interaction between genes and their influence on both drug response and susceptibility to specific diseases, such as cancer.
This genetics-based approach to personalized health is transforming our treatment and management of disease.
Genomic Screening
The first health checkup to include complete genome sequencing, analyzing more than 700 known genetically based diseases.
The future of medicine is written with P

Customized
Having a diagnosis of certainty allows us maximum precision in the treatment.

Predictive
To know the risk of suffering a disease in a healthy person in order to prevent it.

Preventive
Establish a prevention plan to reduce the probability of disease occurrence.

Participatory
It is the patient who decides when and what information he/she wants to know.

Population
Achieve universal accessibility to genetic studies for the entire population.
Advanced Therapies
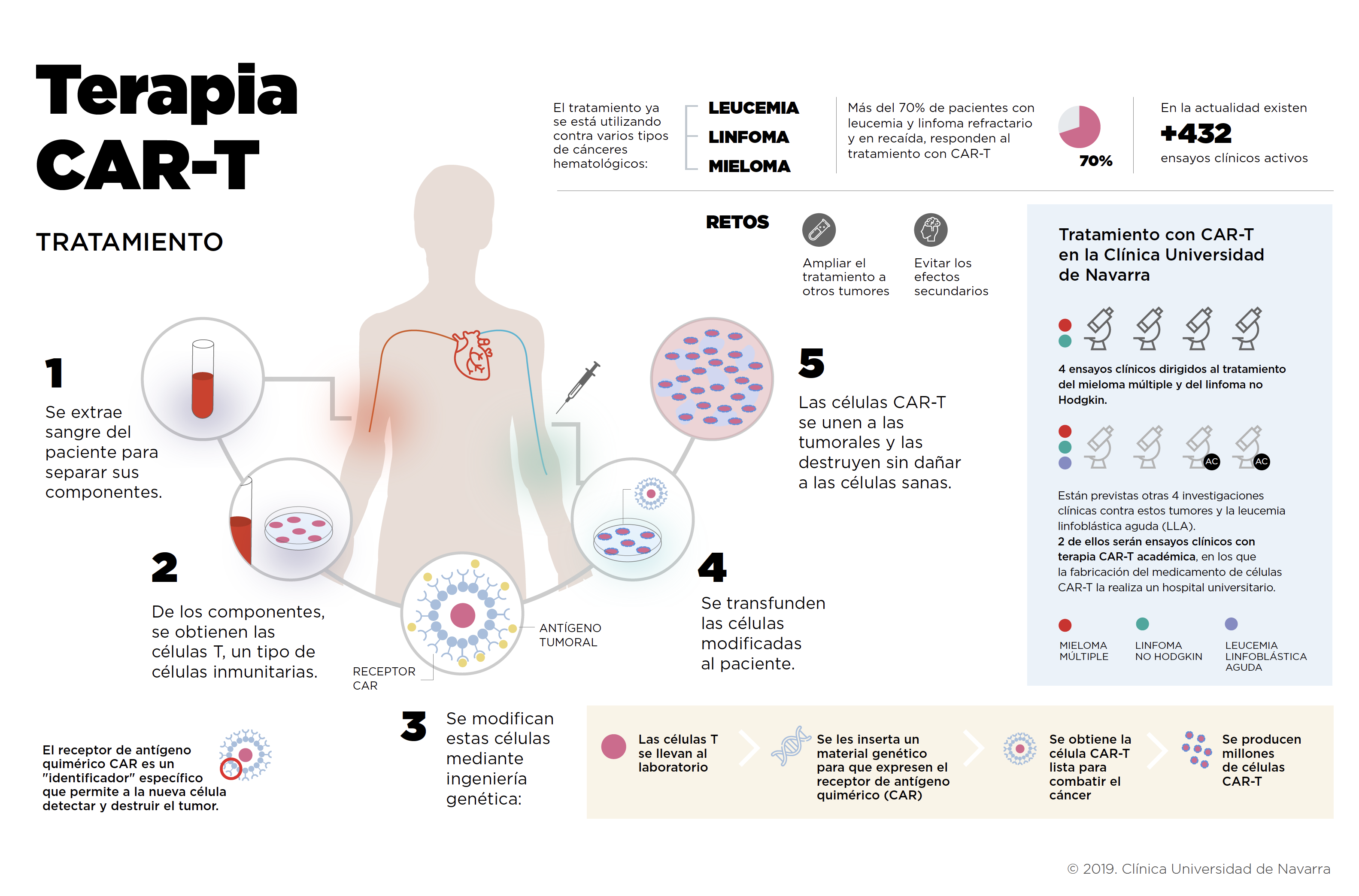
CART cell therapy
CAR-T cell therapy is a novel cellular immunotherapy procedure indicated for some hematological tumors.
It consists of genetically modifying these immune cells to provide them with tools to recognize and destroy tumor cells more effectively.
Pharmacogenetics
Pharmacogenetics makes it possible to personalize treatment, since by knowing the patient's genomic data it is possible to administer a drug at a more effective dose and avoid adverse effects.
In cancer patients, it allows the drug and the exact dose to be administered to the right patient. This greatly increases the chances of obtaining positive results, reducing damage to healthy cells and serious adverse reactions when the drug is administered.
In psychiatric patients, who are usually polymedicated, it allows improving efficacy and adjusting doses.
Gene Therapy
Based on curing some diseases caused by the lack or dysfunction of a gene by replacing it with its correct version.
Progress in techniques for administering these therapies to cells, such as the creation of safer and more efficient viral vectors, has boosted their use in clinical practice, and there are currently several authorized gene therapies.