Pain in the hand
"Rehabilitation and the use of passive or dynamic splints are essential to achieve favorable results".

Hand pain can have multiple causes. The hand is a predilection for wounds and burns caused by objects of work or domestic use. Most serious hand injuries are due to inexperience or failure to take proper precautions in the use of machines or instruments.
The reasons for consultation are often due to injury, pain or deformity. It is important to determine the chronology of symptoms and signs and possible causes.
The exploration is the most important element for the diagnosis. It is also important to perform an exploration of other origins of the symptoms such as: neck, arm, elbow and forearm.
The treatment of hand injuries has as its main objective the recovery of function.

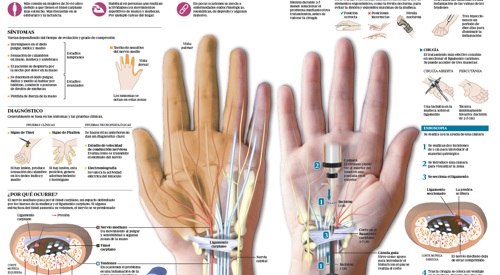
What are the symptoms of hand pain?
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have a problem with your hand
Causes of hand pain
Osteoarthritis is often polyarticular and patients report pain and stiffness predominantly in the morning. The presentation of the arthrosis in the small articulations of the hand is very frequent. In some cases deformities of the fingers appear and very frequently thickening.
The nodules of Heberden in the distal joints and the nodules of Bouchard in the proximal ones are characteristic signs of the arthritis. The most common location is in the distal interphalanges and at the base of the thumb at the trapeziometacarpal joint called rhizosphere.
The rizartrosis produces limitation of the function of the thumb and pain when carrying out activities of clamp with the thumb. In evolved phases and with intense pain if the medical treatments have failed, surgery is resorted to and a resection or substitution arthroplasty can be made. In young people the solution may be an arthrodesis.
Hand fractures are very frequent, especially the phalanges, and the mechanisms of production are multiple: traffic accidents, crushing, sports accidents, games, domestic accidents, etc.
The correct reduction of fractures is important to avoid rotational or angular deformities.
The treatment is orthopedic in the vast majority of cases.
They are very common and if not treated correctly can lead to a prolonged functional disability and even sequelae with great limitation of work capacity. The most frequent causal germ is Staphylococcus aureus. Without effective treatment, the infection can spread proximally and in some cases lead to lymphangitis or septicemia.
The administration of antibiotics according to the antibiogram, hand rest in the acute phase and anti-edema measures such as raising the hand to avoid stiffness are essential. When there is suppuration or collection of pus, it is necessary to surgically drain the abscess without suturing the skin and to initiate early mobilization.
The "trigger" or "spring" finger is produced by the thickening and constriction at the entry level of the digital fibrous sheath that prevents easy sliding of the flexor tendons. When resistance is overcome, a sudden digital movement is produced. In some occasions, the finger can be blocked "deceived finger" with impossibility for the active extension. Besides this sign, the patient suffers a pain in the base of the affected finger.
The conservative treatment with rest and local or systemic anti-inflammatory can solve the problem in some cases, but the preferential treatment is the surgical opening of the digital fibrous sheath.
This disease is characterized by a contracture of the palm due to a fibrosis of the fascia that covers the tendons of the hand. This fibrosis causes retraction in the tendons and, although it is not painful, it can create a great functional incapacity.
Forty percent of patients have a family history of Dupuytren's disease. The right hand is affected in 62% of cases and there is bilateral involvement in 70%. The most affected finger is the ring finger, followed by the little finger.
Besides the familiar predisposition there are other factors that can favor its appearance like diabetes, alcohol, smoking, small traumas, etc.
The usual treatment is minimally invasive surgery that allows to eliminate the fibrotic tissue and thus to allow again the movement of the tendons.
Recently, treatment of the disease has begun with injections of collagenase with excellent results.
Thumb
They are the most common and the most frequent is in the ulnar collateral ligament. Mechanism of abduction and flexion of the finger: thumb abducted in flexion or extension (fall on the hands, stick, ball or direct hit). It is frequent the distal rupture with bone tearing. When there is total injury and proximal displacement and to the dorsum of the adductor is advisable the surgical repair.
Fingers
Metacarpophalangeal joint. The instability is valued in flexion, if there is total injury, surgical treatment is recommended. Interphalangeal joint: they are very frequent and require immobilization for healing.
It is manifested by the inability to flex the distal phalanx (deep flexor), flex the middle phalanx (shallow flexor) and digitally extend it (extender).
Disinsertion of the extensor tendon
It is called "hammer toe". It is produced by a forced and sudden flexion of the distal interphalangeal. The treatment consists in the placement of a splint in extension of the distal interphalangeal and in flexion of the proximal one to relax the tendon, during four weeks. In some cases the tendon drags a bone fragment that, if large, may require surgical reinsertion.
Rupture of the central portion of the extensor tendon
Difficulty in extending the middle phalanx Over time, the Boutoniérè deformity (flexion of the proximal interphalange and hyperextension of the distal interphalange) occurs if treatment consisting of placement of a splint in extension of the proximal interphalange (IFP) has not been carried out. If the injury is not recent or has been produced by a wound, surgical suture is necessary.
Injury of the extensor tendons in the back of the hand
They are very common due to the proximity to the skin.
Flexor tendon injuries
They are very frequent and with a multitude of varieties. The formation of adhesions limits the sliding of the flexor and causes a great functional incapacity. An early passive mobilization of the fingers with dynamic splints is required.
It is very important the postoperative rehabilitation to achieve the mobility of the fingers.
Where do we treat it?
IN NAVARRE AND MADRID
The Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology covers the full spectrum of congenital or acquired conditions of the musculoskeletal system including trauma and its aftermath.
Since 1986, the Clinica Universidad de Navarra has had an excellent bank of osteotendinous tissue for bone grafting and offers the best therapeutic alternatives.
Organized in care units
- Hip and knee.
- Spine.
- Upper extremity.
- Pediatric orthopedics.
- Ankle and foot.
- Musculoskeletal tumors.

Why at the Clinica?
- Experts in arthroscopic surgery.
- Highly qualified professionals who perform pioneering techniques to solve traumatological injuries.
- One of the centers with the most experience in bone tumors.