Herniated disk surgery
"In less than 10% of the cases of disc herniation, the treatment is surgical".
DR. RAFAEL LLOMBART SPECIALIST. ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY AND TRAUMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT

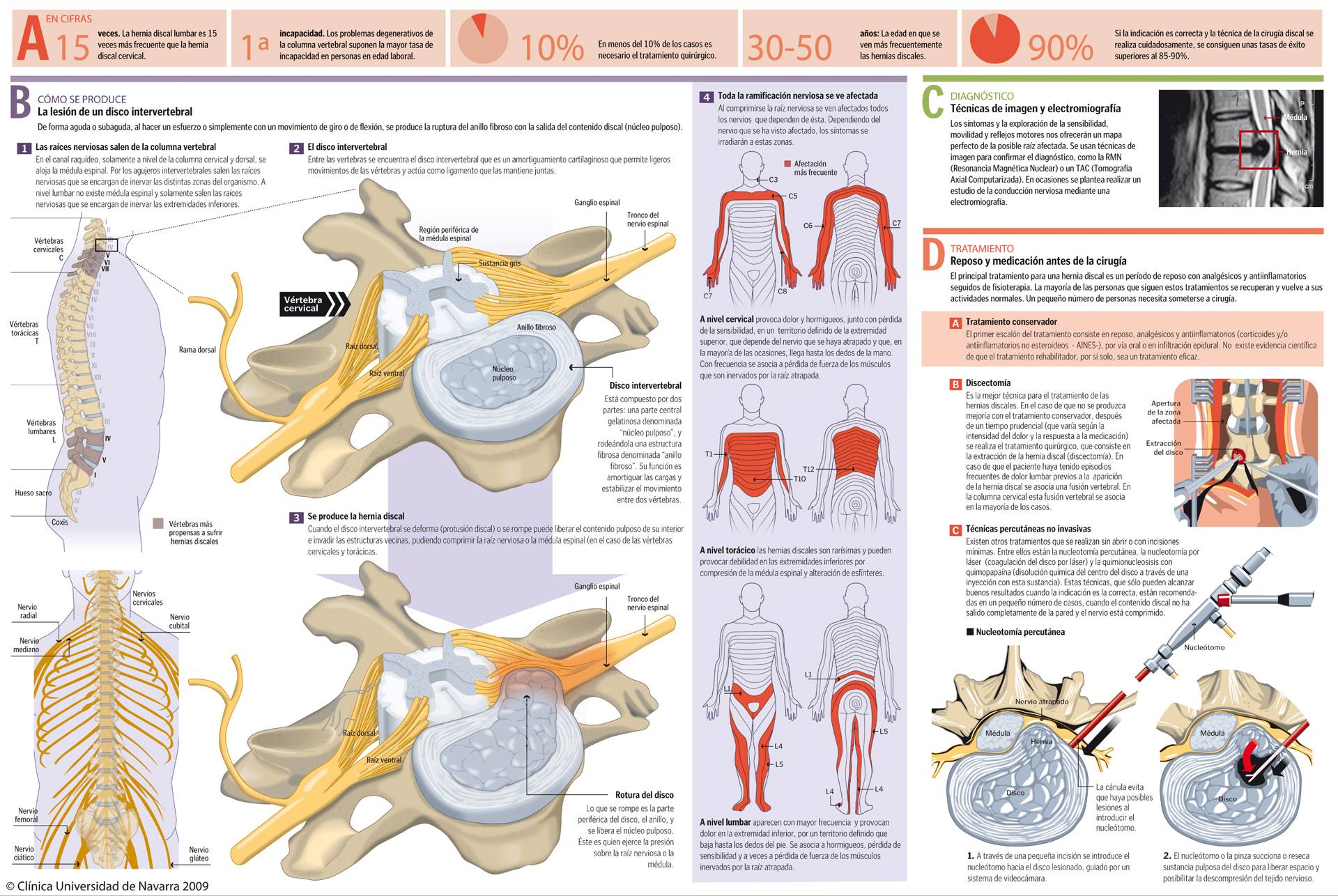
The appearance of a herniated lumbar vertebral disc can lead to pain in the lower back, called lumbago, as well as radiated discomfort in the lower extremity, called sciatica. Precisely, sciatica is the most characteristic symptom of a herniated disc, and the distribution of the pain varies according to the root or nerve that is compressed.
Most patients improve from this condition with conservative treatment. This type of therapy consists of rest, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, infiltrations, etc.
However, surgery is necessary in more than 5% of cases, reaching up to 10% of those affected.
Hence, surgical intervention must be the final resource, only recommended if the patient does not tolerate the pain after 6 or 8 weeks of conservative treatment or if he or she presents progressive loss of strength or sphincter problems.

When is a herniated disk operated?
If the herniation is voluminous and compresses all the nerves it encounters, it can produce what is called cauda equina or ponytail syndrome, which is a surgical emergency.
In most cases, this pain subsides with conservative treatment without surgery. However, approximately 10% of them will require a surgical intervention for their treatment.
In the Clinic we have the most innovative technology for a correct diagnosis and we have extensive experience in performing the latest surgical techniques, with special interest in minimally invasive surgery for a better patient recovery.
Most frequent indications:
Have you been diagnosed with a herniated disk?
Surgical treatment may be necessary
How is disc herniation surgery performed?
About discectomy
It is the best technique for the treatment of herniated discs.
In the event that there is no improvement with the converter treatment, after a prudent time (which varies according to the intensity of pain and response to medication), surgical treatment is performed. This consists of the extraction of the herniated disk (discectomy).
If the patient has had frequent episodes of low back pain prior to the appearance of the herniated disc, a vertebral fusion is associated.
In the cervical spine, this spinal fusion is associated in most cases.
Minimally invasive percutaneous techniques for herniated disc
There are other treatments that are performed without opening or with minimal incisions.
Among them are percutaneous nucleotomy, laser nucleotomy (coagulation of the disc by laser) and chemonucleosis with chemo-papain (chemical dissolution of the center of the disc through an injection with this substance).
These techniques, which can only achieve good results when the indication is correct, are recommended in a small number of cases, when the disc content has not completely come out of the wall and the nerve is compressed.
Other surgical techniques for herniated disc
In certain circumstances, depending on the associated osteoarthritis and previous history of low back pain, in addition to root decompression, a vertebral fusion is performed (either with screws attached to bars or plates, or with boxes in the disc space) that manages to eliminate movement, an effect that improves low back pain.
This technique offers a success rate of close to 80%, although it is assumed as a disadvantage the risk of accelerated degenerative change in the adjacent disc segments which, according to studies by the University of Navarra, has not been shown to be superior to that of the evolution of arthrosis itself.
As an alternative to some vertebral fusions or in cases of disc herniation or degenerative disc affectation, arthrosplasty or complete disc replacement with an artificial prosthesis is used. It is indicated mainly for low back pain, with or without sciatica, mechanical, refractory and discogenic origin.
Arthroplasty can also be indicated for the treatment of the degeneration of the segment adjacent to a fusion already performed. Several series on the results of this technique indicate that the degree of satisfaction in patients exceeds 90% in the short term and, even in the experimental phase, its long-term results are not well known.
Recovery after herniated disc surgery
From then on, you should practice rehabilitation exercises to achieve a good recovery. If the indication is correct and the disc surgery technique is carefully performed, the success rates are higher than 85-90%.
However, it should be noted that, as a result of the operation, it is more likely to improve the pain radiating to the lower limb than lumbar discomfort, especially if the latter had it before. After all, the herniated disc appears in discs that already have degenerative changes, wear and tear and these can continue to give low back pain.
Endoscopic surgery is, in principle, more attractive to patients, but it is not appropriate for everyone. Thus, even though it has been performed for more than 20 years, the gold standard continues to be laminectomy.
Possible complications
All surgeries carry a risk of complications, such as infection and bleeding.
Although some spinal surgeries carry additional risks, such as nerve injury, sphincter alteration or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fistula (leakage), most spinal surgeries are now considered quite safe.
With respect to arthroplasty, it is essential to carefully dissect and protect the large vessels and a nerve plexus located in front of the spine, since in this case retrograde ejaculation could occur in males (2%).
Where do we do it?
IN NAVARRA AND MADRID
The Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology covers the full spectrum of congenital or acquired conditions of the musculoskeletal system including trauma and its aftermath.
Since 1986, the Clinica Universidad de Navarra has had an excellent bank of osteotendinous tissue for bone grafting and offers the best therapeutic alternatives.
Organized in care units
- Hip and knee.
- Spine.
- Upper extremity.
- Pediatric orthopedics.
- Ankle and foot.
- Musculoskeletal tumors.

Why at the Clinica?
- Experts in arthroscopic surgery.
- Highly qualified professionals who perform pioneering techniques to solve traumatological injuries.
- One of the centers with the most experience in bone tumors.