Liver Cirrhosis
"To individualize the risk of each patient, assess the possibility of treatment of the disease causing liver damage and prevent complications, they should be monitored regularly by the doctor".
DR. MIGUEL SOGBE
SPECIALIST. HEPATOLOGY UNIT

Liver cirrhosis is the ultimate consequence of many chronic liver diseases leading to the loss of normal liver architecture and a progressive decline in liver function.
Any disease that causes chronic inflammation of the liver can, over the years, lead to cirrhosis.
There are many causes of cirrhosis. The main ones in our environment are two: the excessive consumption of alcohol (ethyl or alcoholic cirrhosis) and chronic hepatitis C (cirrhosis due to the C virus), which are responsible for 80 percent of the cases of cirrhosis in Spain.
The Clínica Universidad de Navarra offers speed in diagnosis, which is very important in these cases thanks to its advanced imaging equipment.

What are the symptoms of liver cirrhosis?
In the initial stages, patients may be asymptomatic. Progressively, the patient is tired, without energy, without appetite, may have digestive problems and lose weight and muscle mass.
When the disease is advanced, the patient is always ill, cannot lead a normal life and the following symptoms, among others, appear:
- Jaundice. Yellowing of the skin due to the inability of the liver to remove bilirubin from the blood.
- Changes in the skin. Vascular dilations, especially in the cheeks, trunk and arms. In addition, redness may appear on the palms of the hands and finger pads. The nails have a whitish tone.
- Salt and water retention. Accumulation of fluid in the lower extremities (edema) and in the abdomen (ascites).
- Ease of bleeding. When the liver fails, bleeding from the gums and nose is frequent, as well as the appearance of bruises with soft blows.
- Some patients present severe internal bleeding, especially in the digestive system due to broken varicose veins in the esophagus or stomach. These hemorrhages are serious, can be fatal and require admission to a hospital for treatment.
- Changes in behavior and level of consciousness. The liver removes substances from the blood that are toxic to the brain. If the liver fails, these substances produce brain intoxication manifested by nocturnal insomnia, daytime sleepiness, behavioral and mood changes, and disorientation and a progressive decrease in consciousness, which may lead to coma. This complication is serious and requires hospital admission.
- Changes in sexual function. Due to hormonal changes and malnutrition, loss of sexual desire and potency in males and loss of menstruation and fertility in females are common. In addition, in men, they can produce breast enlargement, sometimes painful.
- Malnutrition. The liver is very important in the absorption and use of the nutrients we ingest.
- Therefore, in advanced stages, cirrhotics are malnourished and lose a lot of muscle mass and strength.
- Other complications. Cirrhosis is the most important risk factor for the appearance of liver cancer.
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have cirrhosis of the liver
How is liver cirrhosis diagnosed?
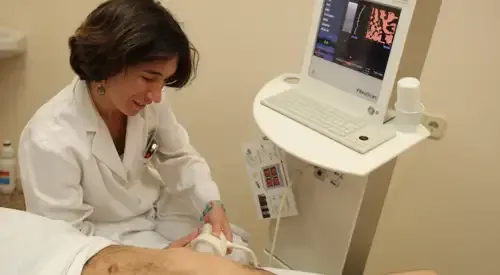
- Medical history: history of alcohol consumption, risk factors for chronic hepatitis B and C (parenteral drug use, sexual promiscuity, sexual partners of patients with Hepatitis B or C), drugs, herbal and homeopathic treatments and drug use; presence of itching in women, pulmonary pathology or family history of liver disease.
- Examination of the patient: presence of hepatomegaly (increase in the size of the liver), splenomegaly (increase in the spleen), presence of skin lesions such as spider veins, telangiectasias on the cheekbones or redness of the palms.
- Analytical studies: alteration in the number of blood cells, markers of liver function or hepatitis B or C virus infections, among others, and study of coagulation.
- Abdominal ultrasound: allows indirect diagnosis in many cases.
The direct diagnosis of certainty is made through liver elastography and liver biopsy.
How is liver cirrhosis treated?
Cirrhosis as such lacks specific medical treatment, since it is irreversible. Some of the diseases that produce it can be treated and the evolution from early stage cirrhosis to advanced stages can be prevented or delayed.
Dietetic treatments
Among the dietetics is the reduction of salt, to prevent fluid retention, and the reduction of proteins (meat, fish) for hepatic encephalopathy. Since good nutrition is necessary, the diet should always be supervised by the physician. Vitamin and mineral supplements are sometimes needed.
Pharmacological treatments
Among the drugs, diuretics are mainly used to treat fluid retention and so-called beta-blockers to prevent digestive bleeding. Many other drugs may be necessary to treat complications, but most of them are used primarily in the hospital setting.
Liver transplantation
The definitive treatment of cirrhosis is liver transplantation. It is performed in patients whose survival is estimated to be less than two years, as a result of that disease, and in those who have no contraindication for performing it for other reasons.
What clinical trials do we have on Liver Cirrhosis?
Where do we treat it?
IN NAVARRE AND MADRID
The Hepatology Unit
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
We are pioneers in the application of gene therapy in the treatment of liver tumors and hereditary metabolic diseases, and we have extensive experience in the diagnosis and treatment of viral hepatitis and in the treatment of liver cancer using radioembolization systems with Ytrium-90 microspheres.
The Clinic is at the forefront in Spain in performing liver transplantation between living people.
Diseases we treat
Treatments we perform
- Hepatic Arterial Embolization
- Partial splenic embolization
- Genetic study in hepatology
- Liver Radiofrequency
- Liver Radioembolization
- Liver resection
- Liver transplantation

Why at the Clinica?
- Highly specialized team of professionals with more than 25 years of experience.
- Nursing team specialized in hepatic patients.
- Important research activity on the molecular mechanisms that cause some of these diseases.









