Vitiligo. Loss of melanocytes
"The best indication for stem cell treatment is localized vitiligo, not large areas, that remain stable and have not responded to conventional medical treatments”.
DR. ALEJANDRA TOMÁS
SPECIALIST. DERMATOLOGY DEPARTMENT

What is vitiligo?
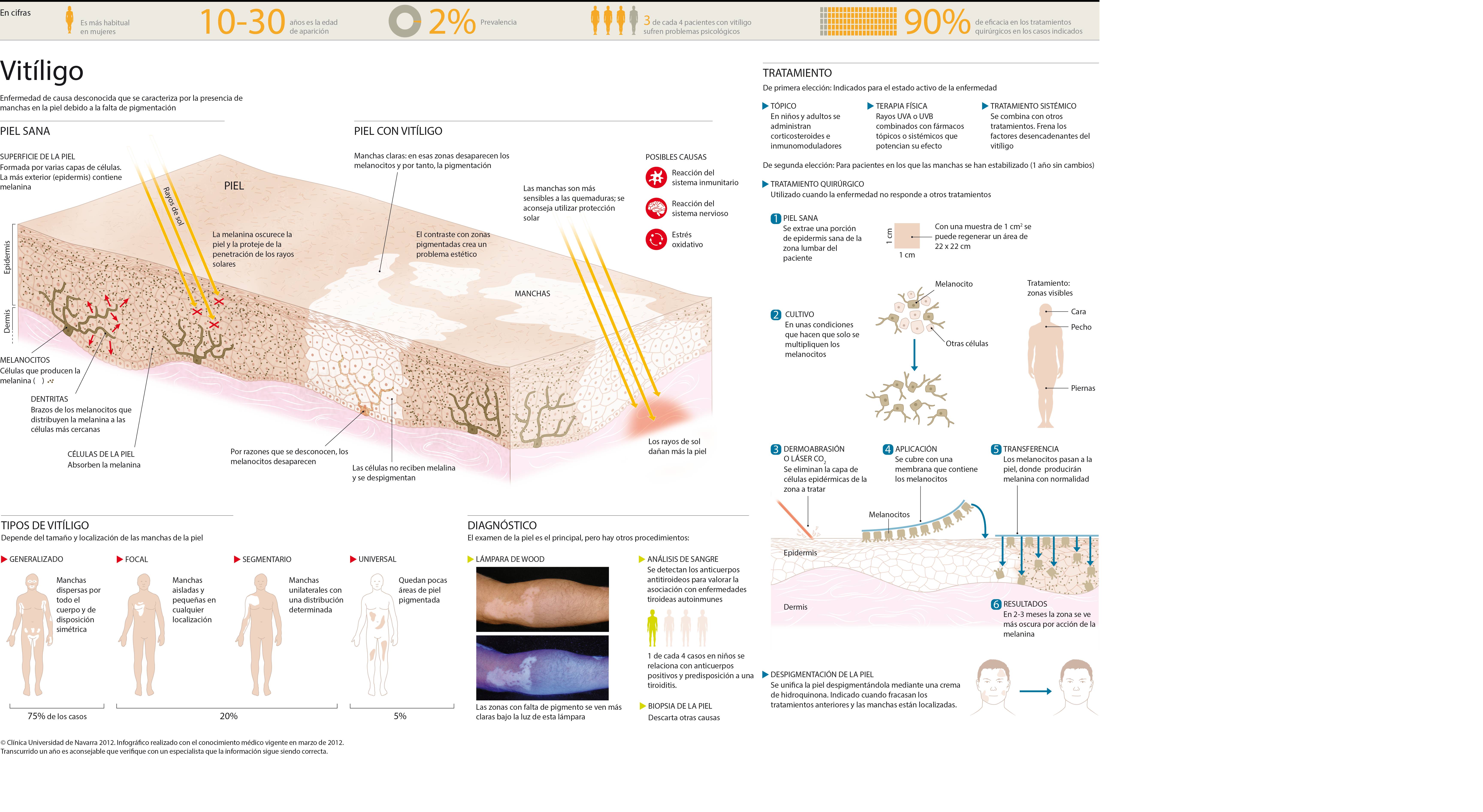
Vitiligo is a skin disorder of unknown cause which is characterized by the presence of white spots due to lack of pigmentation.
It is a disease that affects 1% of the world's population, being more frequent in those races that have a greater amount of skin pigmentation.
It is believed that there is a greater prevalence in women and the age of appearance is between 10 and 30 years, although it can appear at any time of life.
In the indicated cases, surgical treatment is 90% effective, being a highly recommended alternative.

What are the usual symptoms of vitiligo?
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may suffer from vitiligo
What are the causes of vitiligo?
The cause of melanocytes disappearing or ceasing to synthesize melanin is not known exactly.
Different theories have been formulated, highlighting mainly the one that considers this disease to be of autoimmune origin.
It has been observed that situations such as stress or trauma can precipitate the appearance of these lesions in predisposed patients.
Sometimes it is associated with other types of diseases such as diabetes, pernicious anemia, Addison's disease or thyroid diseases.
Types of vityligo
- Focal vitiligo is one in which isolated and reduced size and number of spots appear in any location.
- Segmental vitiligo is characterized by the fact that the macules are unilateral and usually follow a certain distribution. The generalized type is the most common type and is characterized by multiple hypopigmented macules scattered all over the body surface, with a symmetrical arrangement.
- Acrofacial vitiligo affects distal parts and the facial region. The universal form is one in which few pigmented body areas remain.

How is vitiligo diagnosed?
The diagnosis is established in most cases by clinical examination of the patient's skin.
Sometimes, the slit lamp or Wood's lamp can be used. This is an ultraviolet light that makes areas without melanocytes appear bright white.
Sometimes a skin biopsy must be done to rule out other autoimmune diseases, as well as blood tests for thyroid hormones or vitamin B12.
How is vitiligo treated?
Pioneers in the use of cell therapy in the treatment of vitiligo
Powerful corticosteroids can be used in limited areas, but always avoiding chronic continuous application.
In the case of more extensive vitiligo, what is known as oral photochemotherapy is usually used, which consists of the administration of an oral drug (psoralen) plus exposure to UVA rays (PUVA). Repigmentation is sometimes achieved in 50% of the cases.
Another type of treatment used in vitiligo of moderate extension is the application of Kellina topically plus sun exposure. Never more than half an hour. The administration of amino acids such as phenylalanine both orally and topically accompanied by sun exposure is another therapeutic modality used in vitiligo.
Good results have also been obtained with calcipotriol topically, which is a drug used in psoriasis, and with calcineurin inhibitors.
Lately, there is an increasing number of publications about the surgical treatment of vitiligo, using autologous skin grafts or selective melanocyte cultures.
This new technique consists of transplanting the patient's own epidermal cells (skin cells) from a pigmented area to certain areas that appear depigmented.
In general, this cell therapy technique has been applied in those areas where a more satisfactory response is expected, such as the facial region, which is also the one that most often interests the affected people. There are other areas of the body where repigmentation is not so good, such as the hands, where the appearance of vitiligo is also frequent.
The best indication is the treatment of selective areas, not large areas, which remain stable and have not responded to conventional medical treatments.
It is important to note that surgical treatment by epidermal cell slides should never be a first choice treatment for vitiligo and should never be applied in an active vitiligo.
Finally, in those patients where the areas of vitiligo are larger than those of normal pigmented skin, the treatment may consist of depigmentation of the healthy skin by means of topical hydroquinone at high concentrations.
Cell therapy for the treatment of vitiligo is a technique that starts with the culture of epidermal cells, a mixture of keratinocytes and melanocytes, and then proceeds to selective cultures, so that they constitute a monolayer on the amniotic membrane support.
The procedure developed by a team of specialists of the Clinic, begins with the obtaining of a biopsy (small surface of skin) extracted from a hidden zone, as it can be the lumbar region or the buttock, that is pigmented.
The skin sample is then processed in the Cellular Therapy area. There, in an enzymatic way, they separate the epidermis from the dermis to obtain, from the already disintegrated epidermis, the cells necessary for the culture.
The obtained cell units are then cultivated on amniotic membrane until the growth of millions of cells is achieved.
The quantities of epidermal cells obtained from the culture should be processed until sufficient cell surface is obtained to cover the affected area. If the area to be treated is very large, the number of weeks that the epidermal cells must remain in culture will need to be increased. In this way, as many cell plates as required by the affected area are obtained.
The application of the amniotic membranes with the epidermal cells in the patient is performed in the operating room:
- First, the white spots are treated with a CO2 laser. It is necessary to apply the laser in a very superficial way to get rid of the epidermis.
- The amniotic membranes with the epidermal cells are then implanted on this epidermis.
- Once transplanted, the melanocyte layers must be covered by an occlusive dressing that will be removed after 3 or 4 days.
- Next, the patient must be exposed to solar ultraviolet radiation, if it is a suitable time of year, or UVA rays, following a certain protocol.
The surgical technique is ambulatory and is performed under local anesthesia.
In general, this cell therapy technique has been applied in those areas where a more satisfactory response is expected, such as the facial region, which is also the one that most often interests the affected people. There are other areas of the body where repigmentation is not so good, such as the hands, where the appearance of vitiligo is also frequent.
Where do we treat it?
IN NAVARRE AND MADRID
The Department of Dermatology
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Department of Dermatology of the Clinica Universidad de Navarra has extensive experience in the diagnosis and treatment of dermatological diseases.
We have extensive experience in highly precise surgical treatments, such as Mohs surgery. This procedure requires highly specialized personnel.
We have the latest technology for the dermo-aesthetic treatment of skin lesions, with the aim of achieving the best results for our patients.
Diseases we treat

Why at the Clinica?
- Experts in Mohs Surgery for the treatment of skin cancer.
- We have the best technology for dermo-aesthetic treatments.
- Safety and quality assurance of the best private hospital in Spain.