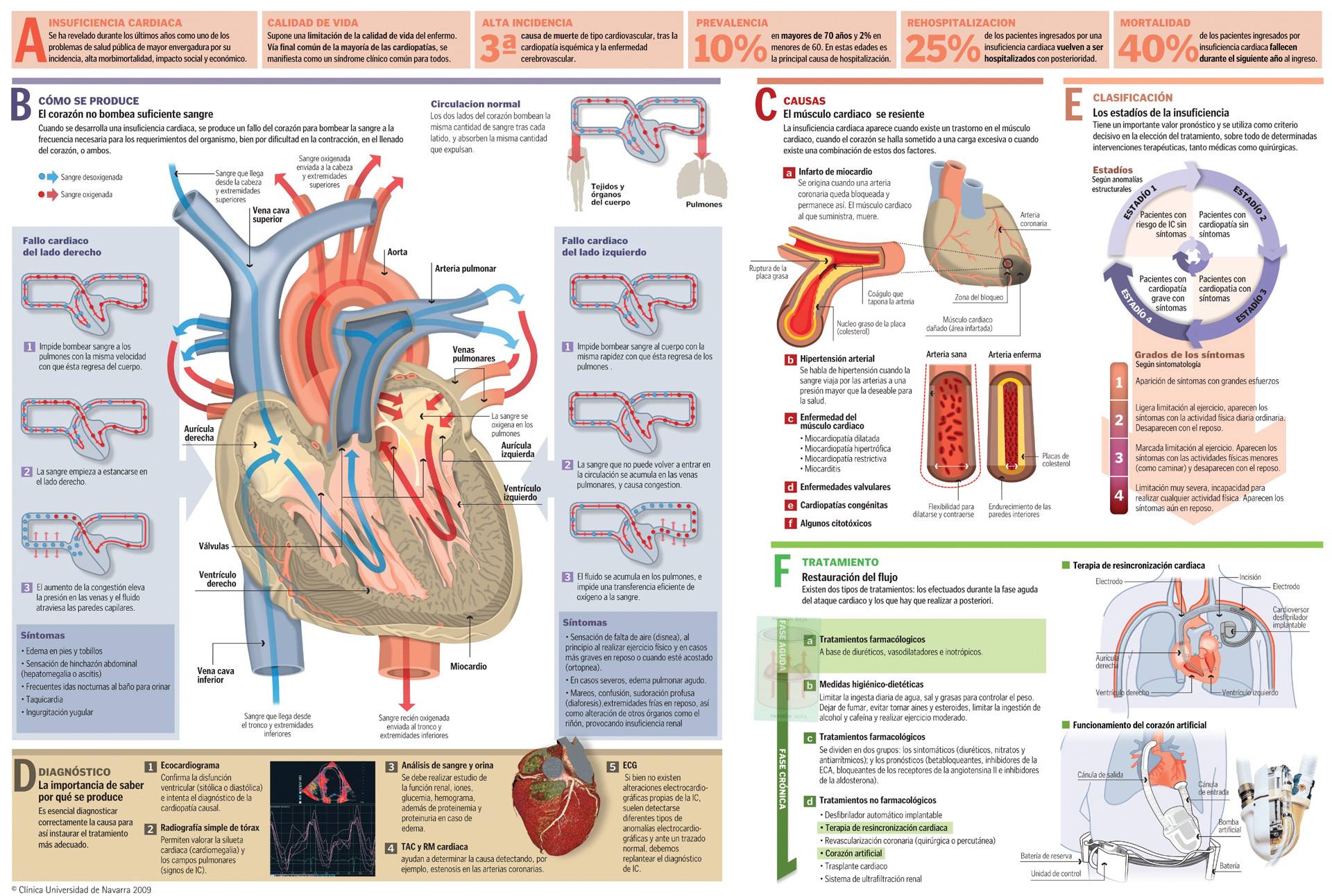
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
"Sometimes the defibrillator is associated with cardiac resynchronization therapy, thus improving the heart failure that the patient sometimes also suffers".
DR. IGNACIO GARCÍA BOLAO DIRECTOR. CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT

Cardiac resynchronization therapy aims to solve the problems of heart rhythm desynchronization that can be generated both at intraventricular and interventricular level, by means of pacemakers.
Biventricular pacemakers stimulate both the right and left ventricles to contract simultaneously, thus solving the problem.
In this way, the biventricular pacemaker manages to improve the symptoms of heart failure.
If it is combined with the use of a defibrillator (defibrillator-synchronizer), it makes it possible to treat potentially malignant arrhythmias that sometimes coexist in the patient with heart failure.

When is resynchronization therapy indicated?
Candidates for this therapy are patients suffering from severe heart failure who also show signs of intraventricular dyscronia.
Heart failure is a syndrome usually caused by a decrease in the ability of the ventricles to contract.
However, in some patients with heart failure, the ventricles not only contract little, but do so in a disordered (unsynchronized) manner.
It is easy to imagine that if they not only contract poorly but also contract out of sync, the performance of the heart function is further impoverished, making the heart failure worse.
These signs can be suspected simply by a simple electrocardiogram, in the presence of intraventricular conduction disorders, such as left branch block, and confirmed by cardiac ultrasound.
Most frequent indications for this treatment:
Do you have unsynchronized heart failure?
You may need to undergo cardiac resynchronization treatment
How is cardiac resynchronization therapy performed?
The procedure for implanting a biventricular pacemaker is very similar to that of a conventional pacemaker. It is usually performed under local anesthesia for almost the entire procedure.
During the implant, an electrode is placed in the right atrium and two electrodes are placed in the ventricles through the subclavian vein: a conventional one in the right ventricle, and a special one in the left ventricle, which is accessed through the cardiac venous system (coronary sinus and its branches).
These electrodes will be permanently lodged in their definitive location, connected to the pacemaker which, in turn, is implanted under the skin in the right infraclavicular region.
Recovery from the operation is rapid and allows for hospital discharge in two or three days. When the batteries run out, approximately every six years, it is necessary to replace the pacemaker.
Where do we do it?
IN NAVARRA AND MADRID
The Department of Cardiology
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Department of Cardiology of the Clinica Universidad de Navarra is a center of reference in different diagnostic techniques and coronary treatments.
We have been the first center in Europe to place a pacemaker by means of a catheterization without the need to open the chest, for cases of severe heart failure.
The Cardiology Department of the Clinic collaborates with the Radiology and Cardiac Surgery Departments to achieve a quick and precise diagnosis of the patient.

Why at the Clinica?
- Specialized Arrhythmia Unit of national reference.
- Unit of Hemodynamics and Interventionist Cardiology equipped with the best technology.
- Cardiac Imaging Unit to achieve the highest diagnostic accuracy.