Insomnia
"It is advisable to go to a specialist to study the case, make the necessary explorations, establish a diagnosis and indicate the appropriate treatment".
DR. ASIER GÓMEZ IBAÑEZ
SPECIALIST. SLEEP UNIT

Insomnia is a difficulty in initiating and/or maintaining sleep, or the feeling of not having slept a good night's sleep. Thus, it is a problem of decreasing the quantity and / or quality of sleep.
This sleep disorder occurs in a third of the population (30%), being more frequent in the elderly, women and people with psychiatric diseases. Most of the cases of insomnia have an acute beginning, coinciding with situations of stress, and tend to become chronic in 60% of the cases.
The sleep is necessary for the good physical and mental state of the individual. A bidirectional relation between the dream and the health exists.
When a person sleeps badly during certain time physical and mental alterations take place that can derive to disease.
We have a Sleep Unit, accredited by the Spanish Sleep Society, with the latest advances in diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders.

What are the symptoms of insomnia?
Insomnia has repercussions on the individual's state of vigilance by producing diminished concentration, lack of physical energy and alterations in behavior and emotions (irritability), which significantly affect their quality of life.
The most common symptoms are:
- Decreased concentration.
- Lack of physical energy.
- Behavior alterations.
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have a problem with insomnia
What are the causes of insomnia?
There are multiple causes of insomnia. Some are frequent and others rare, some are due to environmental influences and others to individual disorders, some are of psychiatric or psychological origin and others organic, some are temporary and others are chronic.
The most frequent causes of insomnia are emotional alterations of a reactive nature and psychiatric illnesses. In general, all those situations of the individual that are accompanied by intense anxiety, worry, psychic tension, anguish, fear or sadness. These insomnia tend to become chronic.
In second place there are those diseases or annoyances of physical origin, that do not allow the relaxation previous to the dream or wakes up to him several times during the night: diseases that produce pains, fever, physical sensations like parestesias, itches, tingles, etc.
Thirdly, there are insomnias related to taking substances. Stimulants (coffee, cola, chocolate, etc.) taken in the afternoon-evening can produce conciliation insomnia. The alcohol produces alterations of the dream with maintenance insomnia (frequent wakes ups) and superficial dream. The individuals who take stimulants, legal or illegal, or those that abuse tranquilizing substances, can also present/display insomnia like effect of the abstinence of those substances.
The same occurs when a person usually takes medication for sleep and one day does not have the medication. On that day, he will probably not sleep. In fourth place are the causes of insomnia due to environmental circumstances: noise, heat, odors, hardness of the mattress, etc. Insomnia is present while those environmental circumstances remain.
There is a reduced number of cases in which the cause of insomnia cannot be known, these are called essential or functional insomnias and their treatment will be symptomatic, generally with hypnotic medication.
Who can suffer from it?
This sleep disorder occurs in a third of the population (30%), being more frequent in the elderly, women and people with psychiatric diseases.
Most of the cases of insomnia have an acute beginning, coinciding with situations of stress, and tend to become chronic in 60% of the cases due to behavioral factors (bad hygiene of the dream) and cognitive (ideas and fears to not be slept) developed by the episode of insomnia.
How many hours of sleep is normal?
Depending on age, structure and sleep time vary. Thus, a newborn baby sleeps about eighteen hours, a young adult about seven to eight hours, an old person about six and a half hours.
In the newborn the REM phase occupies more than 50% of total sleep time, in the adult 25% and in the elderly 20%. From the age of 30 to 60, there is a slow and gradual decrease in the quality and total time of sleep. As the age advances, the dream becomes more fragmented and superficial.
Some people present/display changes in the necessity of dream based on the stations of the year (more necessity in winter and less in summer), in situations of physiological change (adolescence or menopause) by the hormonal changes, and in situations of much tiredness by excess of work or worries, that also increase the necessity of dream like a way to recover of this tiredness.
How is insomnia diagnosed?
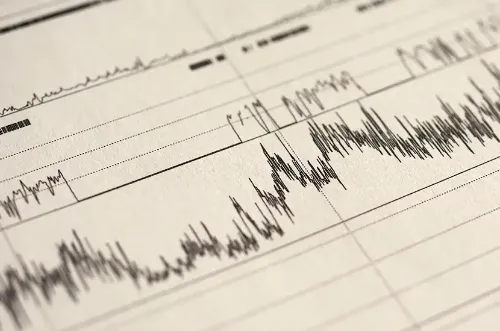
With the advance of sleep study methods, it has been possible to know in depth its physiology and its alterations, but there is still much to know about the psychological functions of sleep.
During the hours of sleep the brain activity changes and these changes are reflected in different electrical waves registered in the electroencephalogram. There are two types of activity well differentiated: the fast activity (of high frequency), similar to which it is given when the subject is awake, that is called dream MOR (fast ocular movements) or paradogical; and the slow activity (waves of low frequency).
These two types of activity are accompanied by physiological cerebral and corporal changes, whose function is the physical recovery and the mental reorganization. During the dream brief wakes up occur, generally accompanied by physical movements, when it is passed of the phase of slow activity to the one of fast activity and vice versa.
Nowadays tests exist able to obtain registries of the dream during all the night that help to establish the diagnosis of the type of insomnia that is suffered, is the polisomnography and other studies of the dream.
How is insomnia treated?
The first solution is to discover the cause and, if possible, eliminate it. If it cannot be eliminated, or while treating the cause, the insomnia should be treated with hypnotic medication.
In case of suffering insomnia for the first time, there is no inconvenience in taking infusions of lime blossom, valerian or other relaxing herbs since they are innocuous and help to sleep better.
In case of slight insomnia the measures of hygiene of the dream can be effective.
Before using drugs for insomnia, it is recommended to apply sleep hygiene guidelines:
- Wake up and go to bed every day at the same time.
- Limit daily time in bed to the necessary sleep time (7.5-8 hours).
- Suspend substances with an activating or stimulating effect on the CNS.
- Avoid long naps during the day.
- Perform physical exercise, avoiding it in the last hours of the day due to its exciting effect.
- Avoid exciting activities in the hours before going to bed.
- Take baths of water at body temperature for its relaxing effect.
- Eat at regular hours and avoid large meals close to bedtime.
- Practice relaxation exercises before going to bed.
- Maintain adequate environmental conditions for sleeping (temperature, noise, light, hardness of the bed, etc.)
Where do we treat it?
IN NAVARRE AND MADRID
The Sleep Unit
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
Accredited by the Spanish Sleep Society, the Clinic's Sleep Unit has the latest advances in diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders.
The joint work of the different medical and surgical disciplines that integrate the Unit of the Sleep of the Clinica does that every patient can be attended approaching his problem of global form, collaborating, if it is necessary, for different specialists.
Diseases we treat

Why at the Clinica?
- We have the best facilities to perform sleep studies.
- Nursing specialized in these disorders for their care and follow up.
- State-of-the-art technology and a highly specialized team.













