Pollen allergy
"At the Clinica we use pharmacological treatment to control the symptoms of pollen allergy and, if the cause has been identified, we start immunotherapy treatment, using vaccines".
DR. GABRIEL GASTAMINZA
DIRECTOR. ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY DEPARTMENT

How do I know if I have a pollen allergy?
Pollen was one of the first allergens to be discovered, and its symptomatology was called "hay fever".
It is a reaction of our organism that perceives as harmful a substance (allergen) that is not. This contact triggers an exaggerated immune response that manifests itself in various organs of the body.
This allergy has a markedly seasonal character.
When pollens absorb moisture, they increase in size and become so heavy that they lose their ability to be airborne. This is why, for pollen-allergic patients, rainy days are the best. On the contrary, the worst days are windy days, especially those with an earthly wind.

What are the symptoms of pollen allergy?
The clinical picture may be mild and of short duration, causing only nasal discomfort or more severe pictures with ocular and respiratory involvement.
It consists of rhinoconjunctivitis, which is characterized by attacks of rhinorrhea (watery runny nose) with intense itching of the nasal mucosa that causes nasal congestion and paroxysmal sneezing.
It is usually accompanied by conjunctivitis with intense tearing, itching, discomfort with light and redness of the eye.
If the condition worsens, it can even manifest itself as bronchial asthma with "wheezing", coughing and difficulty breathing.
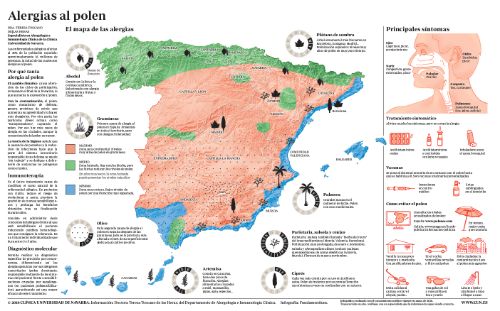
The most common symptoms are:
- Nasal congestion
- Rhinorrhea (increased nasal mucus)
- Sneezing
- Tearing and redness of the eyes
- Dry Cough
- Chest sounds when breathing
- Breathing difficulty
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have a pollen allergy
What are the causes of pollen allergy?
Pollen grains, which are microscopic plant particles, are the allergens that produce the most allergic symptoms. There are three types of allergenic pollens: grass, tree and weed.
In general, trees pollinate from February to April, grasses from May to June and weeds from April or May to September.
It is considered that from 50 grains of pollen per cubic meter, allergic symptoms can appear.
The pollens that most frequently cause allergic rhinitis are birch, poplar, elm, oak, olive, poplar, grasses and shrubs. Grass pollen (appears preferably in summer) is more likely to cause allergy because it is lightweight and easily transported long distances by the wind.
On the other hand, the pollen of most trees (appears preferably in spring) is heavier, settles quickly and you have to be quite close to the tree to inhale it.
Learn what it is and how you can prevent pollen allergy (available in spanish)
How is pollen allergy diagnosed?

The medical history is usually sufficient for the diagnosis of pollen allergy due to its characteristic seasonal pattern.
If one wants to determine specifically the pollen that causes it, skin tests consisting of inoculating the skin with the various suspected allergens and observing whether the characteristic inflammatory reaction occurs are very useful.
The basis of this technique is to reproduce in the skin the reaction that we present in other parts of the organism.
In addition, it is possible to carry out a blood test, with which in a more precise way we can quantify and demonstrate the presence of specific antibodies against that allergen.
In the Clinic we have the possibility of measuring IgE by microarrays, which gives us valuable information about the allergens that the patient recognizes.
How is pollen allergy treated?
Our Immunotherapy Unit is formed by doctors and nurses with great experience in this treatment
The first measure is prevention by avoiding exposure to the allergen, but avoiding pollen is extremely difficult.
Therefore, symptoms are treated with oral or topical antihistamines, preferably the second generation because of their low sedative action. They are effective in reducing itching, sneezing, and runny nose. Nasal decongestants are also effective and often serve to prevent the onset of symptoms.
Patients should also follow some preventive measures.
Sometimes, if the previous treatments are not effective or the patient has an allergy to some specific substance, the cause can be treated with allergy vaccines (immunotherapy), to modify or suppress the allergic response and thus diminish the intensity of the allergic reactions.
Immunotherapy consists of repeated injections of minimal doses of the allergen over a period of 3 to 5 years. After that time, the vaccine achieves in a high percentage of people that our organism stops recognizing that substance as harmful and, therefore, the allergic reaction does not take place. Since there is a risk of allergic reaction, although it is less than 5%, it is administered in the Immunotherapy Units, which are formed by medical and nursing personnel who have sufficient experience to handle these treatments.
At the present time we have a new route for immunotherapy, especially useful in children, which consists of applying drops under the tongue. This avoids punctures and can be applied at home. For a correct prescription of an immunotherapy it is essential to go to the allergist.
Where do we treat it?
IN NAVARRE AND MADRID
Department of Allergology
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Department of Allergy and Immunology of the Clinic is part of the Global Allergy and Asthma European Network, composed of the 25 best departments of Allergy in Europe, chosen for their scientific excellence, multidisciplinary work, teaching and international activities.
We have the most advanced diagnostic techniques, we are at the forefront of research and we collaborate with the best experts. We have more than 50 years of experience in the field.
What diseases do we treat?

Why at the Clinica?
- More than 50 years of experience.
- Pioneers in the technique of molecular diagnosis by microarray.
- Nursing specialized in allergic diseases and their care.








