Cerebrovascular Accident or Stroke
"Few people recognize the signs prior to stroke. Within minutes, it can destroy part of the brain and have permanent consequences if not treated in time".
DR. PABLO IRIMIA SIEIRA
SPECIALIST. NEUROLOGY DEPARTMENT

What is a stroke?
Stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of essential oxygen and nutrients. It is one of the most common reasons for urgent neurological care, caused by a disorder of cerebral circulation.
Every minute that passes, the possibilities of recovery are reduced.
It is one of the most important causes of permanent disability in adults and the second cause of death (the first in women). In addition, it can cause sequels that affect in an important way the quality of life.
For all this, it is vital to go early to a hospital center to establish treatment as soon as possible and take advantage of the neuroplasticity of the brain that makes it easier to recover the affected brain functions in those first hours.
The Neurorehabilitation Unit of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra is made up of a multidisciplinary team of professionals specialized in the rehabilitation of brain damage.
The Clinica has the only cardiovascular checkup that incorporates the highest diagnostic technology by image to precisely quantify its cardiovascular risk
Thanks to the exclusive dedication of our professionals, they allow us to perform the ICAP Checkup in less than 48 hours with a high precision diagnosis.

What are the symptoms of a stroke?
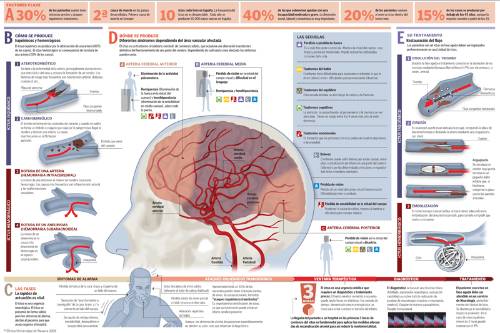
Approximately 30% of patients may have previous, warning, short-lived symptoms called "transient ischemic attacks". It is important to identify them, since they can prevent a subsequent cerebral infarction.
Prevention decreases the risk
Prevention should be done at any age, but especially after 45 years of age, in order to identify risk factors: diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, smoking, heart disease, etc. Its control drastically reduces the risk of stroke.
The most common symptoms are:
- Loss of strength in half of the body (face, arm and leg on the same side).
- Difficulty in speaking.
- Loss of sensation or tingling in half of the body.
- Sudden loss of vision in one eye.
- Very intense headache different from the usual one.
Do you have any of these symptoms?
You may have suffered a stroke
What types of strokes are there?
It can start suddenly or gradually. If the cerebral circulation recovers soon and the stroke lasts less than 2 hours, we speak of a transitory ischemic accident and, in this case, the functional capacity is completely recovered.
Types of ictus or stroke
Cerebral infarction. It is produced by the obstruction of the blood flow in an artery (thrombosis, embolism), which causes a decrease in the blood supply in that part of the brain. Approximately 75% of all strokes are cerebral infarctions. Their consequences in the brain are usually catastrophic, and the symptoms produced are very disabling.
Hemorrhage or stroke. Caused by the rupture of an artery.
The ischemia can take several hours in developing and this time, denominated therapeutic window, is a key moment to avoid or to minimize the cerebral damage.
What are the risks of having a stroke?
Healthy living lowers the risk of stroke.
The risk factors are:
- High blood pressure.
- Heart diseases.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Increased cholesterol.
- Consumption of alcohol, tobacco or drugs (amphetamines, cocaine, etc.)
- Sedentarism.
- Obesity.
How is a stroke diagnosed?

The arrival of the patient to a hospital center within the first 6 hours of the beginning of the stroke is essential to reduce complications by 25-30%.
The diagnosis of the cardiovascular accident (ictus) is based on an assessment by the specialist and, above all, the performance of neuroimaging tests (brain scan and magnetic resonance), ultrasound scan of supra-aortic trunks and transcranial doppler.
The carotid study makes it possible to diagnose whether the cause has been the formation of a thrombus in the blood vessels that has interrupted the flow of blood and, therefore, to assess the more specific preventive treatments, such as a carotid endarterectomy or endovascular therapy.
The Clinic has a team of professionals specialized in cerebrovascular diseases, who have and perform all the necessary imaging tests immediately. In addition, all patients are continuously monitored for early detection of factors that may aggravate the stroke, to establish the appropriate specific treatment and to monitor the evolution.
How is stroke treated?
Treatment of stroke must succeed in restoring blood flow and preventing recurrences
The patient with stroke in the acute phase should be treated in a Neurology service, preferably with a Neurorehabilitation Unit. This decreases mortality and improves evolution.
During the acute phase, treatment consists of dissolving the thrombi that have formed. This can be done in different ways:
- Pharmacological treatment. Fibrinolytic drugs (rt-PA) are applied by venous and sometimes arterial route.
- Surgical treatment. Sometimes it will be necessary to perform a surgical intervention to remove the atheroma plaque formed or dilate the artery by means of an angioplasty with stenting. A catheter is introduced, the tip of which ends in a small inflatable balloon that, when inflated, compresses the plaque against the arterial walls.
- If the stroke is hemorrhagic, the appropriate treatment is the embolization of the aneurysm with colis, substances that block the damaged arteries and prevent it from rupturing again.
Risk factors must also be treated and prevented to avoid the appearance of new episodes: high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes mellitus, etc.
Neurorehabilitation: a dynamic process to achieve the greatest independence
The neurologist and the rehabilitation doctor carry out periodic controls and evaluate the patient, so that together with the physiotherapist, the occupational therapist, the neuropsychologist and the social worker, they achieve the least dependence of the patient in the performance of his activities.
A fundamental part of the treatment is motor rehabilitation, carried out by physiotherapists from this neurorehabilitation unit.
The occupational therapist teaches the patient to improve and optimize the activity remaining after the brain damage and to achieve with it the best adaptation to carry out daily activities, despite the deficit it presents. To this end, compensation strategies are created for the patient to develop basic and instrumental daily activities.
In addition, the job of the occupational therapist and the team responsible for therapy is to advise the patient's family members on how to help him or her incorporate these activities.
When a patient suffers a stroke, there may be a series of sequelae that are important to treat in order to achieve the best possible adaptation in the performance of their daily activities.
There is a great difference between patients with brain damage who follow a neurorehabilitation treatment in a specialized unit, and those patients who do not.
In addition, it is important that both the patient and his/her family know and learn a series of care and advice that can facilitate the patient's adaptation at home.
Where do we treat it?
IN NAVARRE AND MADRID
The Department of Neurology
of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra
The Neurology Department has extensive experience in the diagnosis and multidisciplinary treatment of neurological diseases.
We offer a diagnosis in less than 72 hours, along with a proposal for personalized treatment and post-consultation follow-up of the patient by our specialized nursing team.
We have the most advanced technology for an accurate diagnosis with cutting-edge equipment such as HIFU, deep brain stimulation devices, video EEG, PET and epilepsy surgery, among others.

Why at the Clinica?
- State-of-the-art diagnostic assistance with great work in research and teaching.
- Specialized nursing team.
- We work together with the Sleep Unit.
Our team of professionals
Neurology specialists with experience in treating stroke and its sequelae
undefined
Cardiovascular Checkup
ICAP
INTEGRATED CARDIOVASCULAR
ASSESSMENT PROGRAM
A new approach to cardiovascular risk
The only checkup that incorporates the latest diagnostic imaging technology to accurately quantify your risk of stroke and myocardial infarction.
Thanks to the exclusive dedication of our professionals, we are able to perform the ICAP checkup in less than 48 hours with a highly accurate diagnosis.